Process by Which Polypeptide Chain Is Formed Using Rna
The polypeptide chain then folds and is post-translationally modified. From RNA to Protein.
Proteins Are Functional Molecules Which Support Life And Are Three Dimensional Structures Of Polypeptide Chains Chains Fun Science Dna Sequence Dissociation
At the end of transcription the 5 end of the RNA transcript contains a free triphosphate group since it was the first incorporated nucleotide in the chain.
. The small subunit is responsible for binding the mRNA template whereas the large subunit sequentially binds tRNAs a type of RNA molecule that brings amino acids to the growing chain of the polypeptide. The diagram presents the messenger RNA mRNA molecule as fixed with the 5 3 direction oriented left to right. That transfer RNA molecule leaves the ribosome and goes off to pick up another methionine.
The Ribosome moves along the message from left to right thus the mRNA is read 5 3 or the mRNA passes through the Ribosome in the 5 3 direction. Now the process repeats. The synthesis of a polypeptide however is not equivalent to the production of a functional protein.
Amino Acids Are Added to the C-terminal End of a Growing Polypeptide Chain. In splicing some sections of the RNA transcript introns are removed and the remaining. A newly formed polypeptide contains a signal signal sequence or signal peptide which is a short stretch of amino acids that indicates where in the cell the polypeptide belongs.
Next the ribosome moves along the messenger RNA chain to the next codon. Translation requires two major aids. We have step-by-step solutions for.
The RNA Message Is Decoded on Ribosomes. The ribosome assembles a protein in three steps during initiation the first step transfer RNA tRNA brings the specific amino acid designated by the three-letter code to the ribosome. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA has now been converted to the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Like translating a book from one language into another the codons on a strand of mRNA must be translated into the amino acid alphabet of proteins. The splicing process is catalyzed by protein complexes called spliceosomes that are composed of proteins and RNA molecules called snRNAs. DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation.
The splicing process is catalyzed by protein complexes called spliceosomes that are composed of proteins and RNA molecules called snRNAs. This is the currently selected item. When an RNA transcript is first made in a eukaryotic cell it is considered a pre-mRNA and must be processed into a messenger RNA mRNA.
As RNA polymerase breaks the bonds it synthesises a primary transcript of mRNA using RNA nucleotides. First a translator the molecule. Then the mature mRNA is exported to the cytoplasm where it is translated.
Spliceosomes recognize sequences at the 5 and 3 end of the intron. The Ribosome Is a Ribozyme. Proteins Are Made on Polyribosomes.
Translation is the process of synthesizing a chain of amino acids called a polypeptide. Stop Codons Mark the End of Translation. Textbook solution for Biology.
Elongation Factors Drive Translation Forward. Post-transcriptional processing of the 5 end of the RNA product of DNA transcription comes in the form of a process called the 5 cap. Ribosomes are made up of two subunits that come together for translation rather like a hamburger bun comes together around the meat the mRNA.
These form hydrogen bonds with the exposed DNA strand by. In this way a linear sequence of RNA bases is translated into a linear sequence of amino acids. The ribosome is the site of this action just as RNA polymerase was the.
As a polypeptide chain exits a ribosome it is able to fold into a 3D shape and perform a specific cellular role. Protein biosynthesis starting with transcription and post-transcriptional modifications in the nucleus. At the same time a peptide bond is made between the two amino acids and the first one the methionine breaks away from its transfer RNA.
In the second step elongation each amino acid is sequentially connected by peptide bonds forming a polypeptide chain. How Life Works - Standalone book 2nd Edition James Morris Chapter 19 Problem 5SA. Nucleotide Sequences in mRNA Signal Where to Start Protein Synthesis.
Then rRNA helps bonds form between the amino acids producing a polypeptide chain. Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds. RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand.
During translation the transcribed mRNA is matched with specific tRNA molecules which are each attached to a corresponding amino acid. After a polypeptide chain is synthesized it may undergo additional processing to form the finished protein. This rRNA lies at the heart of the ribosome and catalyzes the transfer of an amino acid bound to a tRNA to the carboxylic acid end of the growing polypeptide chain.
Free RNA nucleotides form hydrogen bonds with the exposed DNA strand nucleotides by complementary base pairing to form a. To be useful polypeptides must fold into distinct three-dimensional conformations. A 5 cap is added to the beginning of the RNA transcript and a 3 poly-A tail is added to the end.
Translation completes the flow of genetic information within the cell. Note that the Ribosome has already encountered the Shine-Delgarno promoter sequence in the. During protein synthesis the order of nucleotide bases along a gene gets transcribed into a complementary strand of mRNA which is then translated by tRNA into the correct order of amino acids for that polypeptide or protein.
Spliceosomes recognize sequences at the 5 and 3 end of the intron. It is essentially a translation from one code nucleotide sequence to another code amino acid sequence. Translation mRNA to protein Overview of translation.
Protein biosynthesis or protein synthesis is a core biological process occurring inside cells balancing the loss of cellular. These amino acids are bound to each other by peptide bonds forming a polypeptide. RNA based catalysis is a conserved feature of polypeptide synthesis and appears to represent an evolutionarily homologous trait.
In translation the instructions in mRNA are read and tRNA brings the correct sequence of amino acids to the ribosome.
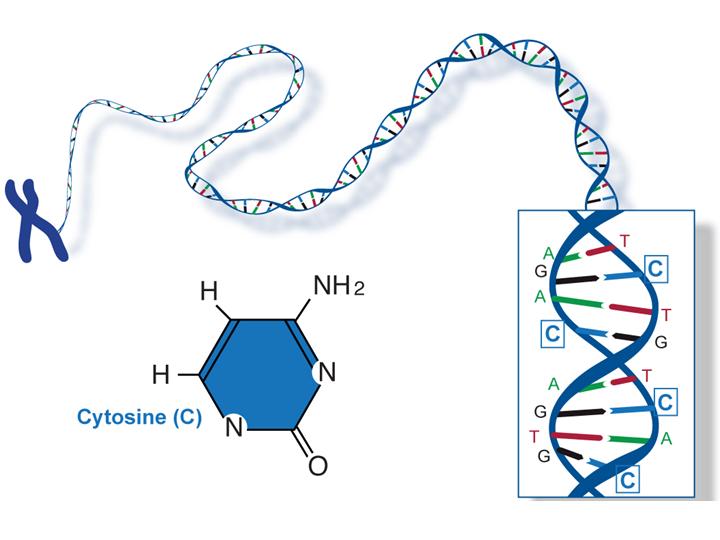
Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica
Protein Synthesis Process And Role Of Dna And Rna In It Earth S Lab
What Is The Flow Of Information From The Dna To A Polypeptide Chain Protein Quora
Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network
Biology Dna Cheat Sheet By Emilyaltmann Http Www Cheatography Com Emilyaltmann Cheat Sheets Biology Dna Cheatsheet Bio Dna Facts Biology Dna
Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology
Transcription And Translation Now That We Know That Dna Is Simply A Code To Produce The Proteins That Do Stuff We Need To Understand How The Proteins Are Made As A Result Of The Dna Existing Firstly The Dna Can Not Leave The Nucleus Secondly The
Stages Of Translation Article Khan Academy
6 4 Protein Synthesis Biology Libretexts
Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica
Trnas And Ribosomes Article Translation Khan Academy
Rna And Protein Synthesis Review Article Khan Academy
Comments
Post a Comment